I built a FPV plane using Ardupilot, DJI FPV system and OpenTX. It can:
Auto Take-off, Navigate Waypoints, Come back home, other autonomous stuff, stream 720p 30ms, record 1080p video.
Its pretty fun to fly. My take off weight is around 686g. I get 15 minutes of flight time with a very old 2200 battery, I need to test with a healthy battery (I’m building a lithium ion pack for it)

Parts List
- Mateksys F765-WSE 70$
- Jumper T Pro /w Internal ExpressLRS 100$
- ExpressLRS PPM Receiver (I was scared that CRSF wouldn’t work)
- Zohd Nano Talon (bought from Amazon long ago..) 150$
- 2200 mAh LiPO 30$
- DJI Fpv system (Caddyx Air Unit + DJI FPV Goggles V2) 500$
- Android Tablet /w QGround Control 329$
- Wifi Access Point 30$
- Esp8266 (telemetry) 1$
How To Build
Well, first you need to read all ardupilot wiki. I used ardupilot for more than 10 years now, since it was APM2.6 with gps module soldered in to the autopilot. It came a long way since then. Here are the steps that I followed:
- Solder the pins of the autopilot, I had to use flux to solder.
- Ideally cut your cables to desired length, it can get messy quick inside the plane.
- Before connecting anything, flash your Mateksys board. You need to install something called Zadig to make the drivers work in Windows. After that you need Inav Configurator (I used 4.1). Start the board while holding boot button. Load local firmware. I downloaded the firmware from this url (bl one). Verify your installation works by connecting the board to mission planner and play with it.
- Connect the GPS (I used TX2,RX2 as it was indicated in Mateksys diagram). It should work out of the box.
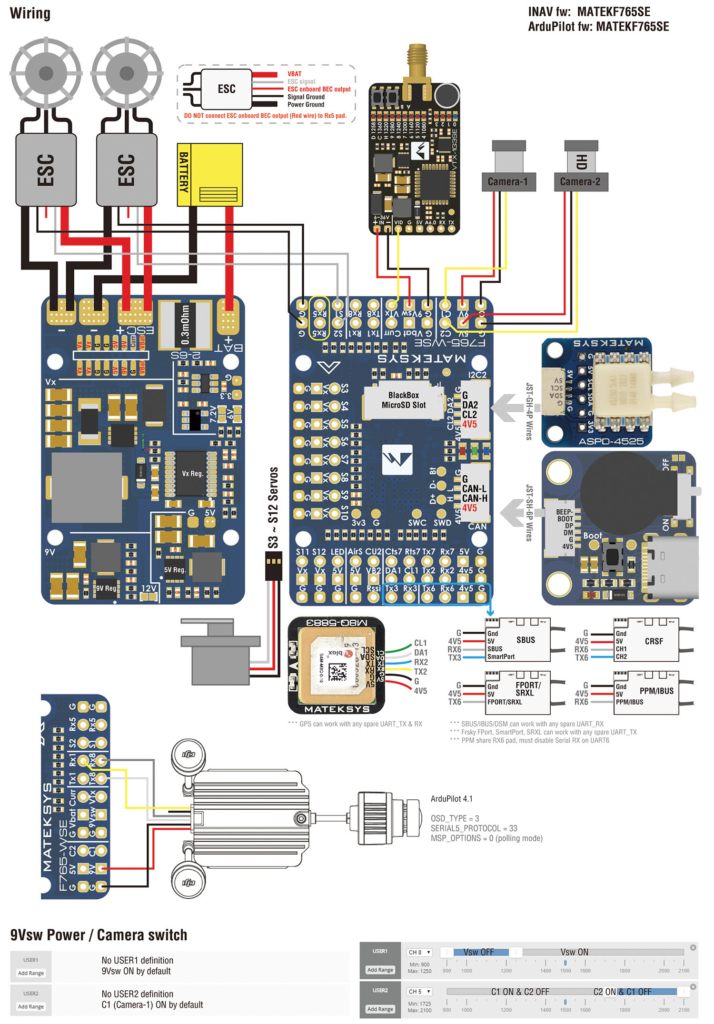
- Wire the controls: I used S3, S4, S5, S6 instead of the default configuration listed in Mateksys website. You need to change the settings for the pins in configuration (TODO add what to do here) I directly wired ESC bec to servo rails, Vx, nothing fried.
- Mount everything cleanly inside the plane!
- Flash the ESP8266 with pixracer firmware. Make sure that you pull the repository with
git clone --recursive https://github.com/dogmaphobic/mavesp8266.gitbecause it has other repositories linked with it, if you don’t you wont be able to compile! You need platformio to compile and flash the project. Also a esp01 flasher with boot button. The unit will not work while connected to the esp01 flasher, after flashing it, remove it from the flasher and wire it to the autopilot as following:
tx1, rx1 –> esp8266,
you need a 5v to 3.3v voltage shifter as well!
(TODO add the settings for the SERIAL_configuration)
after all of this, you should be able to see a wifi access point called pixracer, connect to that and configure it as you wish.
I discovered that AP has very very poor range outside with a tablet. I set up an access point, ESP8266 connects to the access point, and my tablet connects to access point. That way I can get a good bit of line of sight range.
- After making sure that you have WIRELESS TELEMETRY, setup the accelorometer, compass, radio.
- This part is very important, i didn’t do this properly and it lead to a crash.
Switch to manual, put your plane on a bench where it is flat. Look at the control surfaces in the default positions. They should all be flat at manual mode. Adjust the trims accordingly from servo output screen in mission planner.
Yes ardupilot will correct the surfaces in stabilized mode according to your gyroscope, but it takes time for it to do that. When you hand launch you have 1-2 seconds to gain enough speed to start flying. If the autopilot is using those 1-2 seconds correcting its attitude rather than just accelerate, you might fail the take off.
Also make sure that travels of the servos are equal in both directions, you can also adjust your servo arms manually for this as well. - This part is very important too!
Switch to FWBA and tilt/roll the plane. See how the control surfaces react. Roll & Elevator will reach, yaw won’t do anything.
Now command from your controller to see how do control surfaces react, I would do this in manual, fix the controlls as neccessary, you might need to reverse channels. (I assume you already calibrated your radio…) - Now it is time for more configuration! Failsafes, make sure that your throttle failsafe is rock solid and it works. This will save you big time. No failsafe no flight. Also set your battery failsafe.
- Adjust your flightmodes as neccessary. If you don’t want to auto take off, you should use FWBA it is an autopilot assisted flight mode, doesn’t use gps, its like stabilize but with limits.
How to Setup DJI FPV
DJI fpv offers a whole package for the video transmission.
Pros: Works, Low Latency, Long Range
Cons: Restricted (can’t configure OSD very much), Need the goggles, a little expensive.